Ground-Launched Cruise Missiles (GLCMs) are advanced long-range, precision-guided weapons launched from land-based platforms such as Transporter Erector Launchers (TELs), fixed installations, and hardened or concealed silos. Designed for high accuracy and survivability, GLCMs use low-altitude, terrain-hugging flight profiles combined with stealth shaping and multi-mode navigation to penetrate sophisticated air-defence networks and strike deep strategic targets with minimal risk.
They represent a key element of modern land warfare, providing nations with a flexible, cost-effective, and highly survivable strike capability that can be rapidly deployed, dispersed, and concealed across wide geographic areas. GLCMs significantly enhance a country’s ability to conduct deterrence, deep-strike operations, and joint-force missions in contested environments.GLCMs bridge the gap between traditional artillery, surface-to-air missiles, and ballistic missiles—offering a balanced combination of range, flexibility, precision, and survivability at a relatively low operational cost.
Key Characteristics of GLCMs
a) High Mobility and Survivability
-
Mounted on TELs, allowing rapid movement and concealment.
-
“Shoot-and-scoot” capability reduces vulnerability to counter-strikes.
-
Easily dispersed across forests, mountains, or urban landscapes.
b) Terrain-Following Stealth Flight
-
Use terrain contour matching to fly along valleys, hills, and low-altitude pathways.
-
Remain below enemy radar horizons, making detection extremely challenging.
c) Long-Range and High Precision
-
Capable of ranges exceeding 1,000–1,500 km depending on design.
-
Multi-mode guidance ensures pinpoint accuracy against fixed or semi-mobile targets.
d) Versatile Warhead Options
Can be equipped with:
e) Mission Flexibility
-
Can support strategic, operational, or tactical objectives.
-
Useful in anti-access/area denial (A2/AD), suppression of enemy air defences (SEAD), and preemptive strike missions.
Navigation & Guidance Systems of GLCM
GLCMs employ a combination of advanced systems:
-
INS (Inertial Navigation System)
-
GPS/GLONASS/NavIC
-
TERCOM (matches terrain with onboard maps)
-
DSMAC (image-based terminal correlation)
This multi-layered system ensures accuracy even in GPS-denied or jammed environments.
Ground-Launched Cruise Missiles (GLCM)
|
Missile Name
|
Type
|
Range
|
Speed
|
Key Features
|
|
Nirbhay
|
Subsonic LACM
|
1,000 km
|
Mach 0.7
|
Long-range, low-altitude flight, terrain-hugging
|
|
ITCM (Nirbhay Successor)
|
Subsonic LACM
|
1,000+ km
|
Subsonic
|
Indigenous engine (Manik), improved reliability
|
|
BrahMos – Land Attack Variant
|
Supersonic LACM
|
450–500 km
|
Mach 2.8–3.0
|
Very fast, deep penetration, precision strike
|
|
BrahMos – Coastal Defence Variant
|
Supersonic ASCM
|
290–450 km
|
Mach 2.8–3.0
|
Anti-ship coastal battery, sea-skimming
|
|
SMART (ASW Missile)
|
Supersonic ASW system
|
643 km
|
Supersonic
|
Delivers lightweight torpedo to long-range ASW targets
|
|
BrahMos-NG (Future)
|
Supersonic LACM/ASCM
|
300+ km
|
Mach 3
|
Smaller, lighter, for multi-platform use
|
Nirbhay Missile
Nirbhay is India’s long-range subsonic cruise missile capable of striking targets up to 1,000–1,500 km with high precision. Designed for stealthy, low-altitude flight, it uses advanced navigation systems to evade radar and follow complex routes. Carrying a 200–300 kg warhead, it enables deep-strike missions and strengthens India’s conventional deterrence. Its improved successor, ITCM, uses the indigenous Manik engine for enhanced performance.
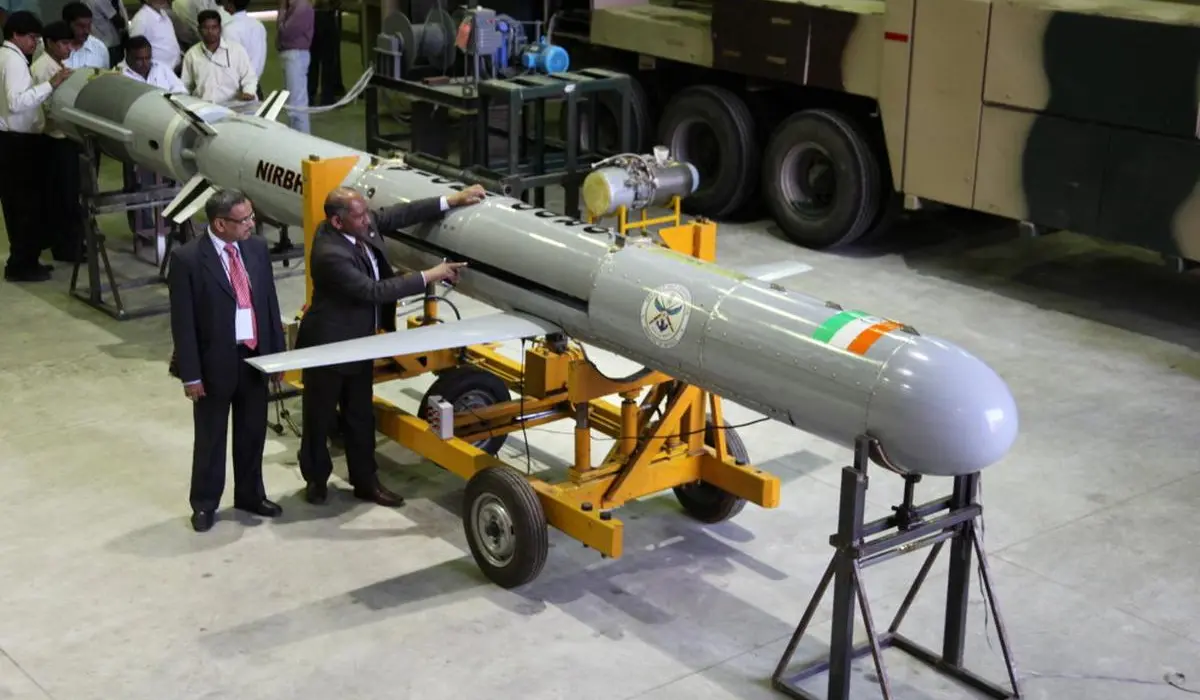

ITCM (Nirbhay Successor)
ITCM (Indigenous Technology Cruise Missile) is the upgraded successor to India’s Nirbhay cruise missile, featuring the indigenous Manik turbofan engine for improved reliability, range, and performance. Designed for long-range, low-altitude, precision strikes, ITCM enhances India’s self-reliance in cruise missile technology and strengthens its deep-strike capability.
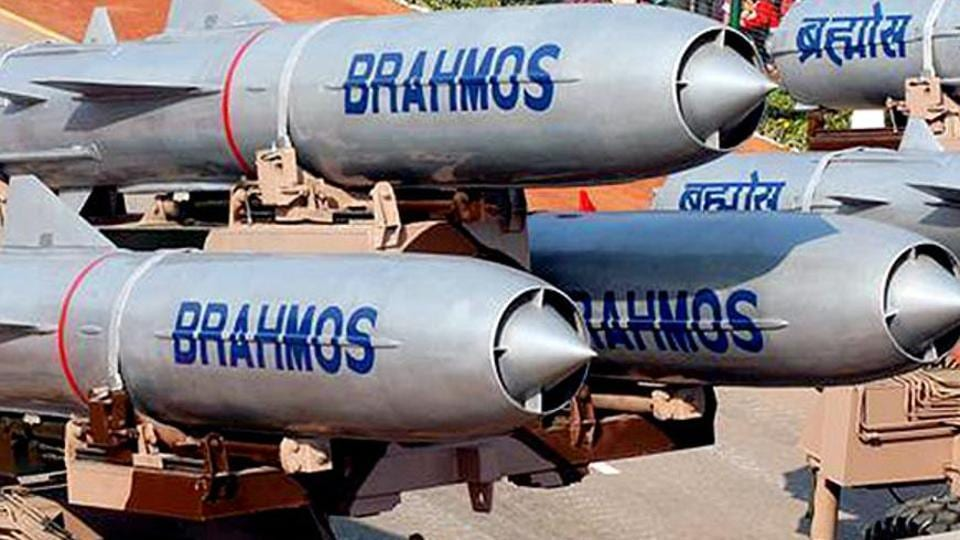
BrahMos – Land Attack Variant
BrahMos – Land Attack Variant is a supersonic cruise missile capable of striking high-value land targets with extreme speed and precision. Traveling at Mach 2.8 – 3 and using low-altitude, terrain-hugging flight, it can destroy command centers, bunkers, and infrastructure from long ranges. Launched from mobile TELs, it provides the Indian Army with a powerful, rapid-response standoff strike capability.

BrahMos – Coastal Defence Variant
BrahMos – Coastal Defence Variant is a supersonic cruise missile system designed to protect coastlines by engaging hostile warships and naval threats at long ranges. Using mobile coastal batteries and terrain-following flight at Mach 2.8–3, it enables rapid, precise, and powerful anti-ship strikes. This variant strengthens India’s coastal security and supports anti-access/area-denial (A2/AD) operations along strategic maritime zones.\

SMART (ASW Missile)
SMART (Supersonic Missile Assisted Release of Torpedo) is an advanced Indian anti-submarine warfare system that delivers a lightweight torpedo to long distances using a supersonic missile. With a range of up to 650 km, SMART combines missile speed with torpedo accuracy, enabling rapid and precise engagement of enemy submarines far beyond the reach of traditional ASW weapons. It significantly enhances India’s maritime security and long-range anti-submarine strike capability.

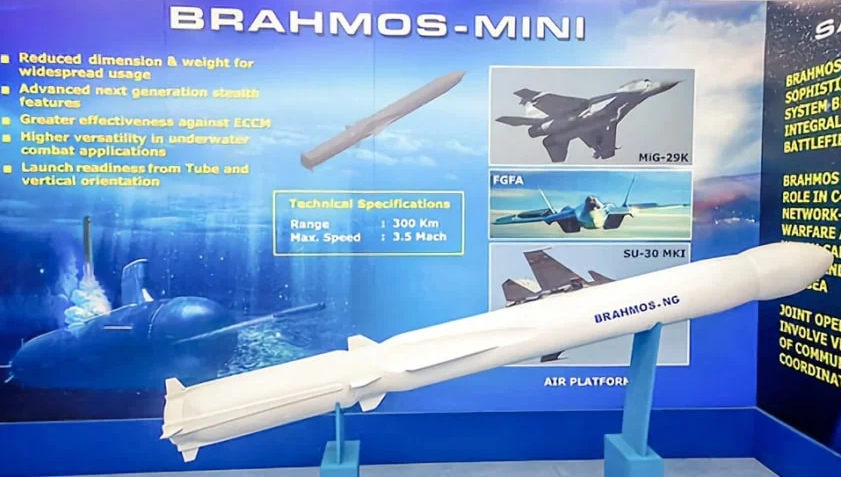
BrahMos-NG (Future)
BrahMos-NG (Next Generation) is an upcoming, smaller, lighter, and faster version of the BrahMos supersonic cruise missile, designed for deployment on a wider range of platforms including fighter jets, helicopters, submarines, and smaller warships. Expected to reach speeds of Mach 3.5 with enhanced manoeuvrability, BrahMos-NG will offer high-precision strike capability with reduced weight and size, allowing multi-missile carriage on aircraft like the Tejas and future AMCA. Once operational, it will greatly expand India's standoff strike flexibility across air, land, and sea domains.

Operational Roles of GLCM
GLCMs are ideal for missions requiring surprise, speed, precision, and stealth. They are used for:
• Deep-Strike Operations
Destroy critical infrastructure far inside enemy territory without exposing land or air units.
• Strategic Deterrence
Provide credible, survivable strike capability that strengthens national defence posture.
• Preemptive and Retaliatory Strikes
Quick-launch capability enables immediate response to emerging threats.
• SEAD/DEAD Missions
Neutralize air-defence radars, missile batteries, and surveillance systems.
• Joint Warfighting
Coordinate with air, naval, and cyber forces for synchronized, multi domain operations.
Their low visibility and high mobility make GLCMs extremely difficult to counter, adding a strategic advantage during conflict.
Advantages of GLCMs
1. Hard to Detect and Intercept
GLCMs fly at extremely low altitudes using terrain masking and stealth shaping, making their radar signature minimal. This low-visibility profile allows them to bypass sophisticated air-defence systems and strike targets with surprise and precision.
2. Highly Mobile and Survivable Platform
Mounted on Transporter Erector Launchers (TELs), GLCMs can relocate quickly after firing or reposition covertly before launch. This mobility prevents enemies from tracking, targeting, or neutralizing the missile system.
3. High Precision with Minimal Collateral Damage
Advanced guidance systems (INS, GPS, TERCOM, DSMAC) ensure accurate strikes, making GLCMs ideal for operations in populated or sensitive regions where collateral damage must be minimized.
4. Cost-Effective Alternative to Air-Launched or Manned Strikes
Because they do not require aircraft, pilots, or large support crews, GLCMs deliver strategic precision strikes at a fraction of the cost of air operations—while eliminating risk to aircrew.
5. All-Weather, Day/Night Operational Capability
GLCMs can function effectively under any weather conditions and at any time of day, ensuring consistent reliability during combat or high-pressure missions.
6. Strategic Flexibility Across Missions
GLCMs can seamlessly transition between offensive roles (deep-strike, preemptive attacks) and defensive roles (deterrence, area denial). This versatility makes them essential in both peacetime posture and wartime operations.
Limitations of GLCMs
1. Subsonic Speed
Slower than ballistic or supersonic missiles, though stealth mitigates this weakness.
2. Requires Detailed Planning
Terrain-following routes and target mapping take time.
3. Vulnerability During Launch
Although mobile, the moment of launch can expose an approximate location.
4. Dependence on Navigation Networks
GPS jamming can affect midcourse accuracy, though TERCOM/DSMAC compensate.
Role in India’s Strategic Doctrine
GLCMs strengthen India’s ability to:
-
Conduct long-range precision strikes with minimal detection
-
Maintain a credible conventional deterrent
-
Respond quickly to aggression without risking aircraft
-
Integrate land-based missile forces into multi-domain operations
-
Counter high-value, well-defended enemy targets
Nirbhay and ITCM are central to India’s long-range strike modernization efforts.
Conclusion
Ground-Launched Cruise Missiles have become indispensable tools in modern warfare, providing a highly survivable, flexible, and precise method for striking strategic targets from secure inland locations. Their combination of stealth, mobility, and long-range accuracy allows forces to conduct deep-strike and deterrence missions with minimal exposure to enemy defenses. As advancements in turbofan propulsion, guidance systems, and low-observable technologies continue to mature, GLCMs will further strengthen national security and play an increasingly critical role in shaping the future of land-based strike strategy and warfare doctrine. For more information about missiles visit Education Masters.
सरकारी नौकरियों, जीके अपडेट्स और करेंट अफेयर्स की ताज़ा जानकारी सबसे पहले पाने के लिए:












.jpg)
.jpg)


