India’s Submarine-Launched Ballistic Missiles (SLBMs) form a crucial pillar of its sea-based nuclear deterrence under the Nuclear Triad. Designed and developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation of India (DRDO), these missiles are launched from nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarines (SSBNs) of the Arihant-class. India currently operates two major types of SLBMs—K-15 missile Sagarika and K-4 missile—each offering different ranges and strategic roles.
Together, they provide India with a stealthy, survivable, and second-strike nuclear capability, enhancing national security and long-term strategic stability. The K-Family missiles represent one of India’s most advanced and strategically significant missile programmes. These missiles form the backbone of India’s second-strike capability under the Nuclear Triad. Named in honour of Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam.
Overview of K-Series Missiles
|
Aspect
|
Details
|
|
Category
|
Submarine-Launched Ballistic Missiles (SLBMs)
|
|
Developer
|
DRDO (Defence Research and Development Organisation), India
|
|
Purpose
|
Strengthen sea-based nuclear deterrence and second-strike capability
|
|
Launch Platform
|
Arihant-class SSBNs & future S5-class submarines
|
|
Missiles Included
|
K-15, K-4, K-5, K-6
|
|
Range Bracket
|
750 km to 8,000 km (varies by missile)
|
|
Propulsion
|
Solid-fuel, canisterised systems
|
|
Key Features
|
Stealthy underwater launch, high accuracy, survivability, nuclear-capable
|
|
Role in Nuclear Triad
|
Ensures concealed, reliable, and secure retaliatory strike capability
|
|
Strategic Importance
|
Enhances India’s maritime security and long-range deterrence posture
|
Key Features of K-Series
-
Underwater launch capability
-
Solid-fuelled, canisterised missiles
-
High accuracy and stealth
-
Designed for flexible nuclear deterrence
-
Compatible with India’s Arihant and future S5 submarines
Importance of K-Series Missiles
-
Strengthens sea-based nuclear deterrence by enabling underwater nuclear strike capability.
-
Provides reliable second-strike capability, ensuring a secure retaliation option.
-
Enhances stealth and survivability through submarine-based concealed launches.
-
Expands India’s strategic strike range from 750 km to 8,000 km depending on the missile.
-
Completes India’s nuclear triad, making the deterrent more credible and resilient.
-
Improves maritime security and regional power projection across the Indo-Pacific.
-
Reduces vulnerability to pre-emptive attacks, as submarines remain hidden underwater.
-
Supports long-term strategic preparedness with upcoming advanced variants like K-5 and K-6.
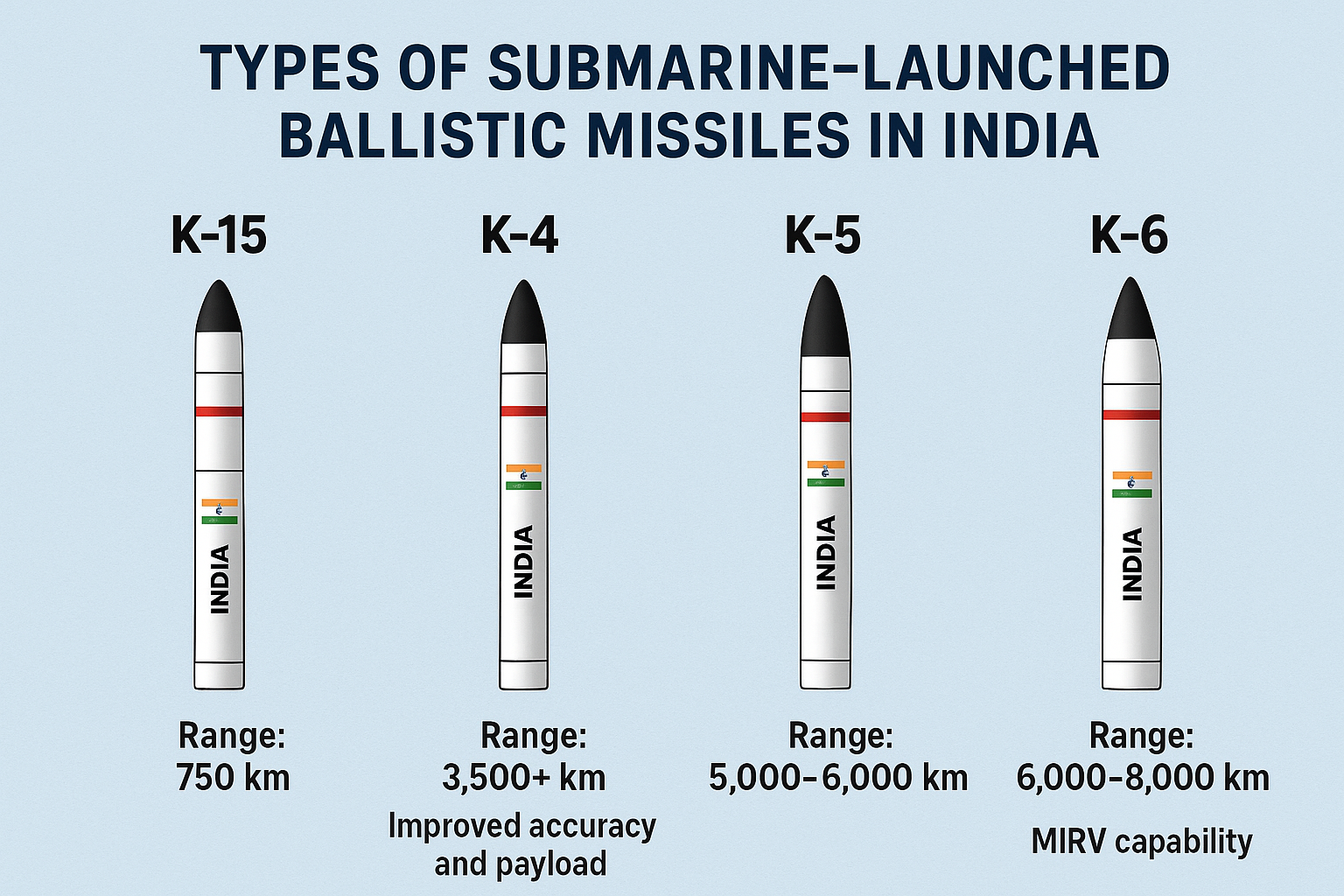
Types of Submarine-Launched Ballistic Missiles(SLBMs)
|
Missile
|
Range
|
Warhead / Payload
|
Propulsion
|
Guidance System
|
Status
|
Notes
|
|
K-15 missile (B-05 / Sagarika)
|
750 km
|
1,000 kilograms payload (strategic or conventional)
|
Solid-fuel, 2-stage
|
satellite navigation and INS
|
Operational
|
Deployed on INS Arihant-class SSBNs; India’s first operational SLBM.
|
|
K-4 missile
|
3,500 kilometers
|
2,000 kg payload; capable of strategic warhead
|
Solid-fuel, 2-stage
|
Advanced INS + astro-navigation + satellite aid
|
Tested / Pre-deployment
|
Designed for Arihant-class & future SSBNs; fills gap between K-15 and ICBM class.
|
|
K-5 missile
|
5,000–6,000 km (expected)
|
Multiple independently targetable payload capability (expected MIRV-capable)
|
Solid-fuel
|
Advanced INS; improved terminal guidance
|
Under development
|
Will significantly expand India’s sea-based deterrence.
|
|
K-6 missile
|
6,000 to 8,000 kilometers (projected)
|
MIRV-capable, heavier payload
|
Solid fuel with 3-stage
|
Next-gen INS + advanced decoys and penetration aids
|
Development / Future SSBNs
|
Expected to be deployed on S5-class submarines; India’s most powerful planned SLBM.
|
K-15 Missile/(Sagarika)
K-15 missile is India’s first operational SLBMs with a range of 750 km. Developed by DRDO, it is deployed on the Arihant-class submarines to provide a reliable short-range sea-based nuclear strike capability. Its compact size allows multiple missiles to be carried onboard.
K-4 Missile
K-4 missile is a medium-range SLBMs with a range of 3,500+ km, designed to bridge the gap between K-15 missile and longer-range ballistic missiles. It offers improved accuracy, better payload capacity, and greater survivability, enabling submarines to strike deep inland targets from the Indian Ocean.
K-5 Missile (Under Development / Proposed)
The K-5 missile is a next-generation SLBMs expected to have a range of 5,000–6,000 km, significantly extending India’s strategic reach. It aims to give India true intercontinental capability from sea, enhancing the SSBN fleet’s deterrence power.
K-6 Missile (Upcoming / Advanced Program)
K-6 missile is India’s most advanced SLBMs concept, with an expected range of 6,000–8,000 km and potential MIRV capability. Designed for future SSBNs, it is intended to provide long-term second-strike capability with global reach and greater penetration against missile defenses.
Purpose of K-Series Missiles
-
Strengthen sea-based nuclear deterrence.
-
Ensure second-strike capability in case of enemy attack.
-
Allow stealthy underwater operations using SSBNs.
-
Provide long-range strike options across regions.
Limitation of K-Series Missiles
-
High development and testing cost due to advanced underwater-launch and composite technologies.
-
Limited deployment because India currently has only a small number of operational SSBNs.
-
Shorter range in early variants like K-15, reducing deep-strike capability.
-
Technological maturity is evolving, especially in guidance, accuracy, and MIRV potential.
-
Dependence on submarines, meaning deterrence weakens if SSBN availability is low.
-
Low production rate because SLBMs require specialized manufacturing.
-
Operational secrecy restricts open evaluation, making performance verification difficult.
Operational role of K-Series missile
-
Sea-Based Nuclear Deterrence
-
Assured Second-Strike Capability
-
Extended Strategic Reach
-
Stealthy and Mobile Launch Platform
-
Deterrence Against Regional and Distant Threats
-
Continuous Nuclear Readiness
-
Strengthening the Nuclear Triad
Conclusion
India’s K-series SLBMs—K-15 Missile, K-4 Missile, K-5 Missile, and K-6 Missile—form the backbone of its sea-based nuclear deterrence and significantly enhance the credibility of its second-strike capability. Each missile in the series brings increasing range, accuracy, and technological sophistication, ensuring India can respond effectively to strategic threats from secure underwater platforms. Together, these SLBMs provide layered deterrence, strengthen maritime security, and support long-term strategic stability, making them a critical component of India’s nuclear triad and overall defense posture.For more information about missiles visit Education Masters.
सरकारी नौकरियों, जीके अपडेट्स और करेंट अफेयर्स की ताज़ा जानकारी सबसे पहले पाने के लिए:





.png)
.jpg)
.jpg)


